Windows 10 Crypto API Spoofing
Microsoft has released a new security patch for a vulnerability that could affect millions of Windows 10 Users world wide.
A decades old API
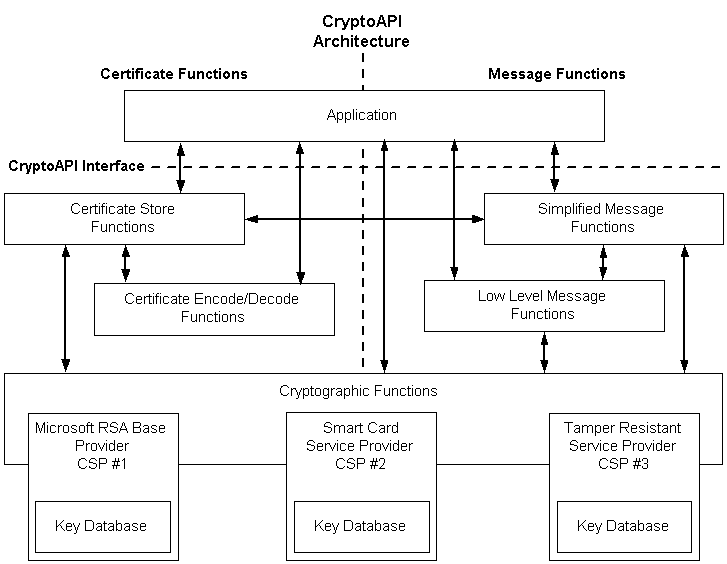
The decades old CryptoAPI tool validates and signs packages/software which could be utilized by hackers/developers to sign and execute illegitimate software thus would allow users to run anything without user’s nor Antivirus/Internet Security software’s notice.
Microsoft mentioned that the vulnerability could also allow hackers to change or modify encrypted communications.
It’s important to mention that CryptoAPI is a legacy API that’s being replaced by a new CNG (Cryptography Next Generation API) which also supports CryptoAPI.
CryptoAPI Key Storage Architecture
Download Patch
Direct Download
https://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/Search.aspx?q=KB4528760
CVE
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-0601
Windows 2008 R2, Windows 7 RDP
A day ago Microsoft released two very important security patches on May 14, 2019.
One of these patches has been detected in the RDP service (CVE-2019-0708) which affects Windows 7 and Windows 2008 R2.
According to MS’s Article a remote code execution vulnerability exists in Remote Desktop Services – formerly known as Terminal Services – when an unauthenticated attacker connects to the target system using RDP and sends specially crafted requests.
No Authentication or Interaction needed
This vulnerability is pre-authentication and requires no user interaction. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could execute arbitrary code on the target system.
An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.
When look at CVE-2019-0708, which is related to the RDP service, we see that attackers are able to run code on systems by sending specially produced packages without any user interaction and authentication and manage to install malware like Ransomware or other execution files.
Download Patch
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2019-0708
Windows 2008R2, 2012R2, 2016 and 2019 DHCP
The other one is in the DHCP service (CVE-2019-0725), and both vulnerabilities are very critical.
A memory corruption vulnerability exists in the Windows Server DHCP service when processing specially crafted packets. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code on the DHCP server.
Download Patch
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2019-0725
Sources:
Microsoft, NSA, Other Security Researchers
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0014_thumb.png)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0024_thumb.png)
![clip_image003[4] clip_image003[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0034_thumb.png)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0044_thumb.png)
![clip_image005[4] clip_image005[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0054_thumb.png)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0064_thumb.png)
![clip_image007[4] clip_image007[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0074_thumb.png)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0084_thumb.png)
![clip_image009[4] clip_image009[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0094_thumb.png)
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0104_thumb.png)
![clip_image011[4] clip_image011[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0114_thumb.png)
![clip_image012[4] clip_image012[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0124_thumb.png)
![clip_image013[4] clip_image013[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0134_thumb.png)
![clip_image014[4] clip_image014[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0144_thumb.png)
![clip_image015[4] clip_image015[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0154_thumb.png)
![clip_image016[4] clip_image016[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0164_thumb.png)
![clip_image017[4] clip_image017[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0174_thumb.png)
![clip_image018[4] clip_image018[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0184_thumb.png)
![clip_image019[4] clip_image019[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0194_thumb.png)
![clip_image020[4] clip_image020[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0204_thumb.png)
![clip_image021[4] clip_image021[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0214_thumb.png)
![clip_image022[4] clip_image022[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0224_thumb.png)
![clip_image023[4] clip_image023[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0234_thumb.png)
![clip_image024[4] clip_image024[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0244_thumb.png)
![clip_image025[4] clip_image025[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0254_thumb.png)
![clip_image026[4] clip_image026[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0264_thumb.png)
![clip_image027[4] clip_image027[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0274_thumb.png)
![clip_image028[4] clip_image028[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0284_thumb.png)
![clip_image029[4] clip_image029[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0294_thumb.png)
![clip_image030[4] clip_image030[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0304_thumb.png)
![clip_image031[4] clip_image031[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0314_thumb.png)
![clip_image032[4] clip_image032[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0324_thumb.png)
![clip_image033[4] clip_image033[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0334_thumb.png)
![clip_image034[4] clip_image034[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0344_thumb.png)
![clip_image035[7] clip_image035[7]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/clip_image0357_thumb.png)