Active Directory Admin Password
We had a security lab on Azure with 12 machines, It included 2 DCs and 10 other machines of different OS and had RDP closed on all the machines except one machine to use.
The Password was set for something simple however it seems that someone has changed it and no one was able to access the domain controller anymore nor any of the machines.
I had another user created for backup but it seems that user was also changed.
The usual method of resetting Azure VM is going through portal or PowerShell
Resetting Via Azure Portal
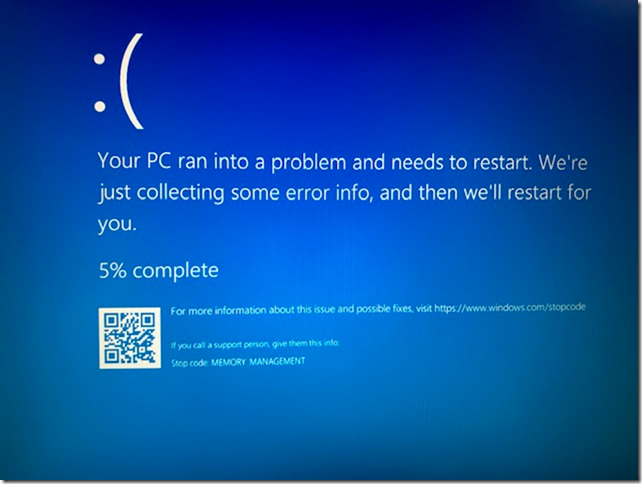
When you try to reset the password from Azure Virtual machine itself. If the VM has Domain Controller it will fail to reset the password with the following error:
Failed to reset RDP configuration
VM has reported a failure when processing extension ‘enablevmaccess’. Error message: “VMAccess Extension does not support Domain Controller.” More information on troubleshooting is available at https://aka.ms/vmextensionwindowstroubleshoot
Through PowerShell
To reset a password, we first need to define the VM we’re working with. To do this, we can use the Get-AzureRmVm cmdlet. I’ll go ahead and assign variables to both the VM name and the resource group since we’ll need to reference those later, as well.
$vmName = 'YOURVMNAMEHERE' $resourceGroupName = 'YOURRGHERE' $vm = Get-AzureRmVm -Name $vmName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName
Next, we’ll need some way to pass the username and password into the script. A great way to do that is through the Get-Credential cmdlet.
$credential = Get-Credential
Once the credential is saved, we can then execute the command to actually make the password change using the variables we set earlier. Notice we had to use the GetNetworkCredential() method on the pscredential object. This method will not work if the credential is retrieved from another computer or from another user account. This shouldn’t be a problem, though, since you’re likely to execute this in a single script.
$extensionParams = @{
'VMName' = $vmName
'Username' = $Credential.UserName
'Password' = $Credential.GetNetworkCredential().Password
'ResourceGroupName' = $resourceGroupName
'Name' = 'AdminPasswordReset'
'Location' = $vm.Location
}
$result = Set-AzureRmVMAccessExtension @extensionParams
Once this completed (hopefully successfully), the VM will need to be rebooted. We can do that by using the Restart-AzureRmVm cmdlet.
$vm | Restart-AzureRmVM
While this PowerShell script might work with a normal VM, It will not work with a DC and would result in the same error as in the portal.
Solution
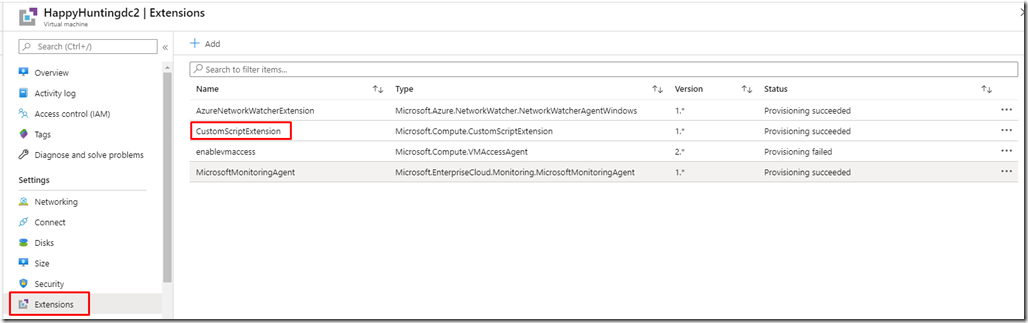
The solution is to write a script which would run through the CustomScriptExtension that you can deploy from the Azure Portal on the intended VM that has the Domain Controller Deployed on it.
Once you get the script ready to change the administrator Password you can upload the script and deploy it.
Let’s get the script ready and demonstrate these steps one by one.
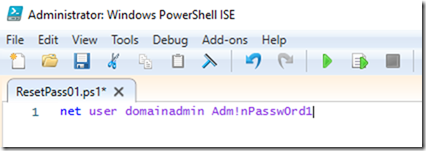
– On my Computer I will write a tiny script that will say
Net User domainadmin Adm!nPassw0rd1
– Save the file on your desktop for later use. Go to Azure Portal, Virtual Machines and select your Domain Controller.
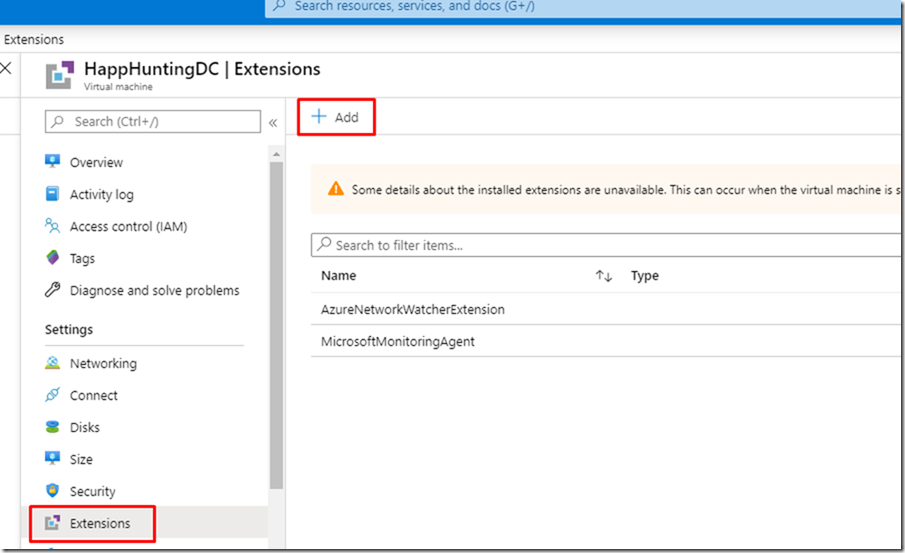
– Go to Extensions.
– Click on Add
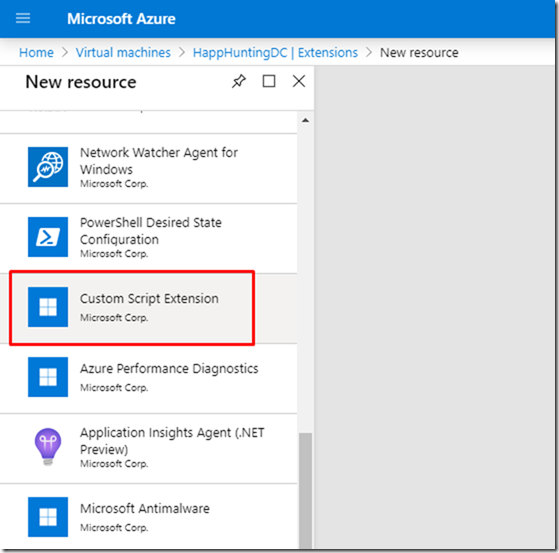
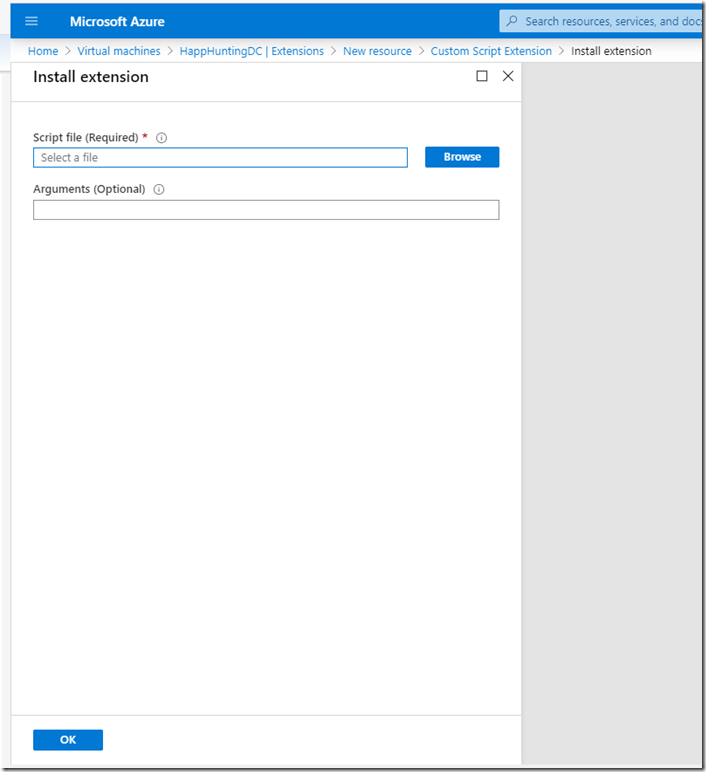
– Select Custom script Extension
– Click Create
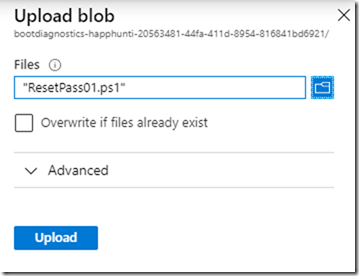
– Browse the PowerShell script on your Desktop.
– Select Storage Account
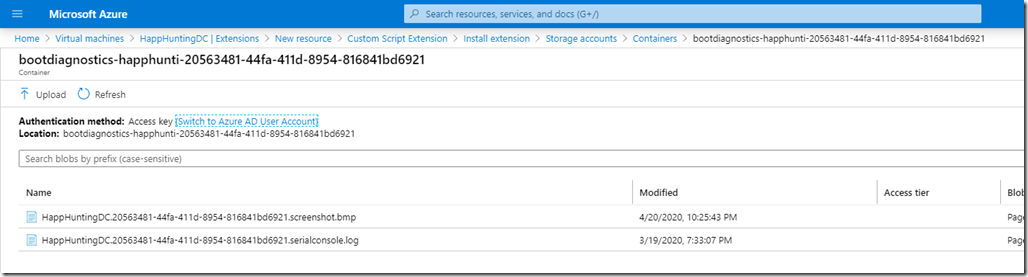
– Select an existing container or create new one
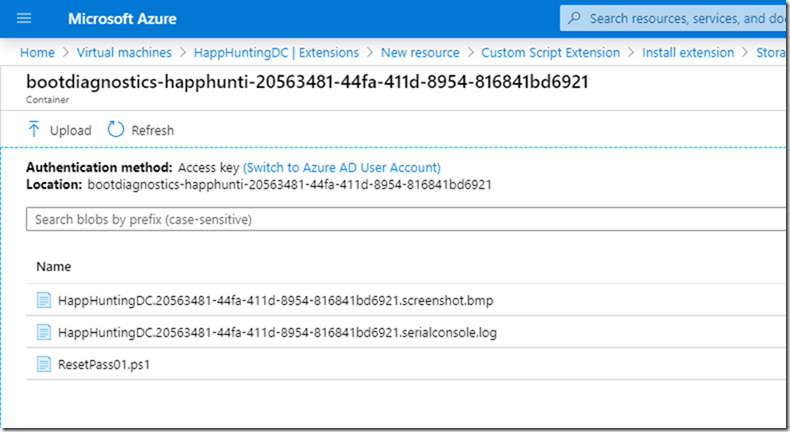
– Upload the file to the container
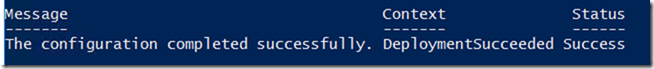
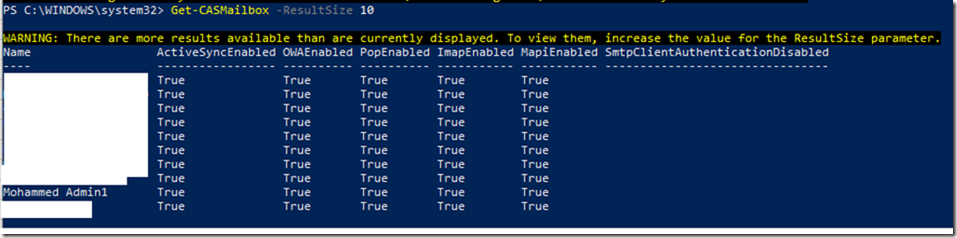
Result
Once deployed, it’ll take few mins to reset the password and you don’t have to restart the server.
Through PowerShell
After this I was able to access the machine again using the new password in the script.
ref:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/run-command
https://mcpmag.com/articles/2017/12/13/azure-vm-password-with-powershell.aspx


![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0014_thumb-2.png)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0016_thumb-1.png)


![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0014_thumb-1.png)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0024_thumb.png)







![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0014_thumb.png)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://www.moh10ly.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/clip_image0016_thumb.png)